Consumer engagement is a cornerstone of business success, and statistics reflect its undeniable impact. According to Salesforce, 84% of customers say the experience a company provides is just as important as its products and services. In a world where choices are abundant, businesses can no longer rely solely on product quality; they must engage consumers on a deeper, more personalized level. A PwC study found that 73% of customers point to experience as an important factor in their purchasing decisions, second only to price and product quality. Research by Bond Brand Loyalty reveals that 79% of consumers are more likely to continue doing business with companies offering loyalty programs. These programs enhance consumer retention by delivering value through rewards, discounts, and personalized offers, fostering a deeper connection between the consumer and the brand.
The Evolution of Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs have significantly evolved over the past few decades, transforming from simple point-based systems into sophisticated, data-driven tools designed to foster deeper connections with consumers.
(1) Traditional vs. Modern Loyalty Programs
Traditional loyalty programs were often straightforward: consumers earned points for purchases, which they could later redeem for discounts or rewards. While these programs drove repeat purchases, they lacked personalization. According to McKinsey, 58% of loyalty programs initially focused on transactional benefits, failing to engage customers on a more meaningful level. These basic programs operated primarily through physical cards and limited consumer data collection.
However, as technology advanced, so did the sophistication of loyalty programs. Modern loyalty programs have transitioned beyond mere points-based systems to include personalized rewards, exclusive experiences, and real-time engagement. A Bond Brand Loyalty report highlights that 68% of consumers now want brands to tailor rewards to their unique preferences, reflecting the demand for more personalized experiences.
(2) The Shift to Data-Driven, Personalized Experiences
The rise of big data, AI, and machine learning has revolutionized loyalty programs by enabling brands to analyze vast amounts of consumer data. Modern loyalty programs are increasingly data-driven, allowing companies to understand purchasing behaviours, preferences, and even predict future needs. For example, Accenture reports that 91% of consumers are more likely to shop with brands that recognize them and provide relevant offers and recommendations.
This shift is not just about rewarding transactions but fostering relationships. Brands like Starbucks and Amazon have integrated loyalty programs with mobile apps, using data to deliver personalized recommendations and real-time offers. Starbucks’ loyalty program, for instance, has been instrumental in increasing sales, with 27 million active members in the U.S. alone, according to Starbucks Q2 2023 earnings report.
(3) The Role of Technology in Loyalty Programs
Technology has been the driving force behind the evolution of loyalty programs. Mobile apps, artificial intelligence, and blockchain have reshaped how loyalty programs function. Mobile-first programs allow for real-time engagement, location-based offers, and seamless reward redemption, while AI and machine learning provide hyper-personalized recommendations.
Blockchain technology is also enhancing the transparency and security of loyalty programs. A study by Capgemini found that 87% of consumers are concerned about data privacy in loyalty programs, making blockchain an appealing solution for secure, transparent reward systems. It allows brands to create immutable, tamper-proof loyalty records, fostering trust between consumers and companies.
The Role of the Modern Supply Chain in Consumer Engagement

A report by Gartner reveals that 63% of supply chain leaders now prioritize improving customer experience, demonstrating the vital role supply chains play in consumer engagement.
(A) Agility, Efficiency, and Transparency
Today’s consumers expect fast, accurate, and seamless experiences across all touchpoints, including delivery and fulfillment. Modern supply chains have evolved to meet these expectations, prioritizing agility to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer preferences. A study by McKinsey found that companies with agile supply chains are 7% more likely to achieve higher revenue growth than those with less agile systems.
Efficiency has also become crucial as consumers demand faster delivery times. According to Statista, 80% of shoppers expect same-day shipping, forcing companies to streamline their logistics and inventory management systems to ensure timely fulfillment. Automation, AI-powered demand forecasting, and real-time data analytics have made it possible to optimize supply chains for greater speed and accuracy.
Transparency has become a significant factor in building trust with consumers. With growing interest in sustainability and ethical sourcing, consumers want more visibility into where products come from and how they are made. A Label Insight survey found that 94% of consumers are more likely to be loyal to a brand that offers complete transparency. Technologies like blockchain and IoT provide real-time tracking capabilities, allowing consumers to see the entire journey of their products, from manufacturing to delivery.
(B) Key Touchpoints for Loyalty Program Integration
As modern supply chains become more consumer-centric, loyalty programs can be seamlessly integrated at various stages to enhance engagement and satisfaction:
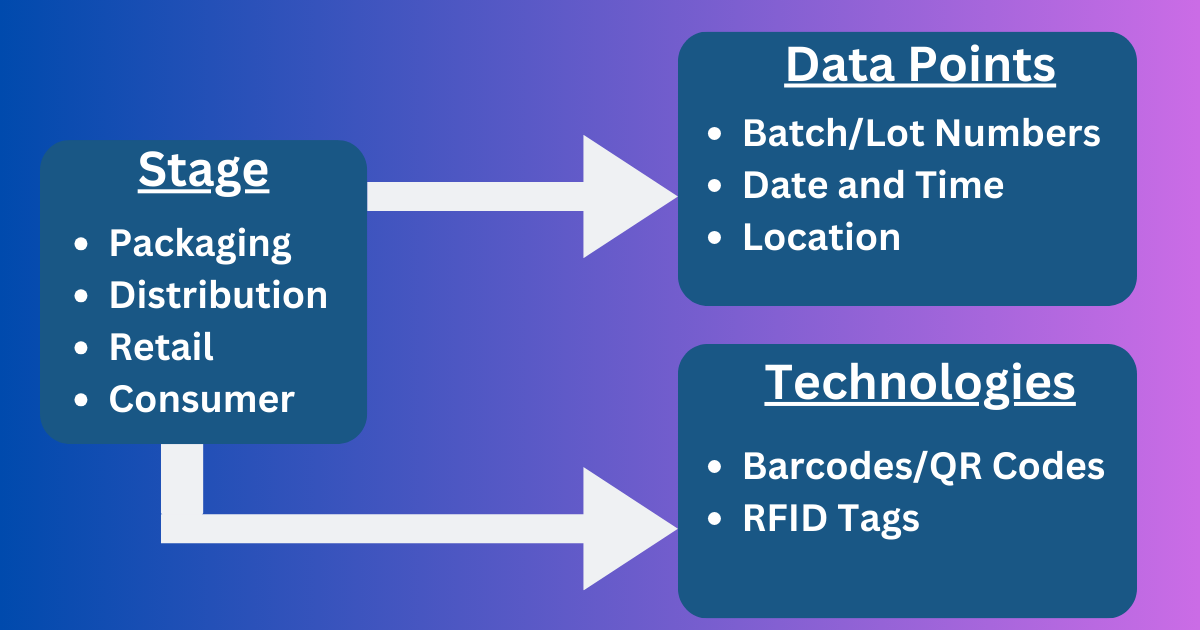
(1) Product Tracking: Modern consumers demand visibility into the status of their orders. Integrating loyalty programs with real-time product tracking can enhance consumer engagement. For example, brands can reward customers for tracking their deliveries or sharing feedback on delivery experiences. A survey by MetaPack reveals that 96% of consumers say a positive delivery experience influences their loyalty to a brand.
(2) Personalized Delivery Experiences: Personalization has become an expectation, with 80% of consumers more likely to do business with a company that offers personalized experiences, according to Epsilon. Supply chains can now offer personalized delivery options, such as choosing delivery times, locations, or even eco-friendly options. Loyalty programs can reward consumers for selecting these preferences, further enhancing their engagement and satisfaction.
(3) Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Consumers appreciate knowing whether a product is in stock or when it will be available. Integrating this with loyalty programs allows brands to reward customers for waiting on back-ordered items or pre-ordering products. According to KPMG, 67% of consumers said that real-time product availability information affects their purchasing decisions.
Benefits of Loyalty Programs Integration with Supply Chain

The integration of loyalty programs into supply chain operations offers a host of benefits, not just for consumers but for businesses as well. By combining personalized experiences with operational efficiency, companies can boost consumer satisfaction, streamline processes, and reduce costs. Here’s how this integration creates value:
1. Enhanced Consumer Satisfaction through Personalized Experiences
Today’s consumers expect personalized experiences at every stage of their interaction with a brand. When loyalty programs are integrated with supply chains, companies can tailor delivery options, rewards, and communications to individual consumer preferences. For example, offering consumers the choice of same-day delivery or rewards for choosing eco-friendly shipping methods creates a unique experience that builds satisfaction and encourages repeat business.
2. Greater Visibility into Product Availability and Delivery Timelines
Visibility into the supply chain is a growing priority for consumers. In fact, Accenture found that 87% of consumers want to track the status of their orders in real-time. By integrating loyalty programs with supply chain systems, companies can offer consumers greater transparency about product availability, delivery timelines, and potential delays. Loyalty programs can reward customers for opting into real-time updates or provide bonuses for patiently waiting on delayed items. According to Gartner, 76% of supply chain professionals cite customer visibility as a key driver for improving customer satisfaction.
3. Building Long-Term Relationships through Proactive Engagement
Integrating loyalty programs with supply chains enables businesses to engage with consumers proactively, rather than reactively. Brands can use predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs, offering personalized recommendations, restock alerts, and exclusive deals based on past purchases. A study by HubSpot shows that companies using proactive engagement strategies enjoy an average increase in customer retention of 72%.
4. Operational Efficiencies and Cost Savings for Companies
Loyalty program integration with supply chain operations doesn’t just benefit consumers; it can also drive significant operational efficiencies and cost savings for companies. Loyalty programs that offer incentives for selecting eco-friendly or flexible shipping options can further reduce logistics expenses. Additionally, automated systems for loyalty rewards reduce administrative costs, allowing companies to allocate resources more efficiently.
5. Data Collection and Refinement of Both Loyalty Programs and Supply Chain Decisions
One of the greatest benefits of integrating loyalty programs with supply chains is the ability to collect and analyze consumer data to inform better decision-making. A Forbes Insights study found that 66% of companies say they can leverage loyalty data to better understand customer preferences, which then drives more informed supply chain and marketing decisions. For instance, if loyalty data reveals a preference for faster shipping, companies can adjust their supply chain processes to meet this demand.
Future Trends in Loyalty Programs and Supply Chain Integration

The integration of loyalty programs with supply chain operations is evolving, driven by technological advances and shifting consumer expectations. Here are some key trends shaping the future of loyalty programs and supply chains, backed by statistical insights:
1. The Rise of Omnichannel Loyalty Strategies
Consumers now engage with brands across multiple channels, from physical stores to e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and social media. Omnichannel loyalty strategies aim to unify these experiences, providing seamless reward opportunities no matter how or where customers interact with the brand. According to Harvard Business Review, 73% of consumers use multiple channels during their shopping journey, emphasizing the importance of omnichannel approaches. Brands that adopt omnichannel loyalty strategies see increased consumer engagement and retention.
2. Sustainability and Ethical Consumerism: Driving Greener Supply Chains
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability and ethical practices are taking center stage in loyalty programs and supply chain management. A Nielsen study found that 81% of global consumers feel strongly that companies should help improve the environment. As a result, loyalty programs are evolving to reward consumers for making eco-friendly choices, such as selecting green delivery options, supporting sustainable products, or participating in recycling programs.
3. Hyper-Personalization and Predictive Engagement
The future of loyalty programs lies in hyper-personalization, where rewards and engagement are tailored to the individual consumer’s preferences, behaviours, and needs. Leveraging AI, machine learning, and data analytics, businesses can predict what a consumer will want next and offer highly relevant incentives at the right time. Predictive engagement is a key aspect of this trend, with companies anticipating customer needs before they are explicitly expressed. For example, by analyzing consuming patterns, a retailer can predict when a consumer will run out of a product and offer loyalty points or discounts to encourage a timely reorder.
4. The Increasing Importance of Experience-Based Rewards and Perks
Consumers are increasingly valuing experiences over material rewards, and loyalty programs are evolving to reflect this shift. Experience-based rewards, such as exclusive events, VIP access, and personalized services, are becoming more common in loyalty strategies. A Bond Brand Loyalty study found that 79% of consumers prefer experiential rewards over transactional benefits like discounts or points, especially in industries like travel, hospitality, and luxury retail.
Case Studies: Successfully Integrating Loyalty Programs into Supply Chain Operations
1. Sun Pharma: Enhancing Patient Loyalty through Integrated Supply Chain Solutions
Sun Pharma, one of India’s largest pharmaceutical companies, has successfully integrated loyalty programs into its supply chain operations, focusing on patient-centric engagement. The company’s loyalty program, “Sun Pharma Care”, is designed to offer patients long-term benefits like discounts on medications, timely refills, and access to healthcare services. According to a report by IQVIA, pharma companies that focus on patient-centric supply chains can boost retention by up to 30%, which Sun Pharma has leveraged to build stronger relationships with patients.
2. UltraTech Cement: Leveraging Loyalty for Better Contractor Engagement
UltraTech Cement, a leading cement manufacturer in India, has integrated loyalty programs with its supply chain operations to build strong relationships with contractors and distributors. UltraTech’s “UltraTech Cement Rewards” program offers contractors and builders incentives such as cashback, discounts, and loyalty points that can be redeemed for construction-related products and services. According to Cement Industry Outlook, optimizing supply chain operations for real-time order fulfillment can increase customer satisfaction by up to 20%, a result that UltraTech has seen with its loyalty-integrated supply chain.
3. UPL: Loyalty-Driven Supply Chain Efficiency in Agrochemicals
UPL (United Phosphorus Limited), a global leader in agrochemicals based in India, has implemented a loyalty program designed to support farmers while also improving its supply chain efficiency. The “UPL Kisan Loyalty Program” rewards farmers with points for purchasing UPL products, which can be redeemed for farm tools, educational workshops, and other agricultural resources. According to Frost & Sullivan, agrochemical companies that utilize supply chain optimization tools can reduce costs by up to 15%, a benefit UPL has realized through its data-driven loyalty strategy.
It’s Time to Digitalize Your Supply Chain
The integration of loyalty programs with supply chain operations, driven by technological advancements, is transforming consumer engagement. By leveraging AI, data analytics, and real-time inventory tracking, companies are able to create personalized experiences that not only enhance customer loyalty but also drive operational efficiencies. As we move into this new era of consumer engagement, the fusion of loyalty programs and supply chain optimization will continue to be a game-changer for brands across industries.




 Engaging Channel Partners
Engaging Channel Partners